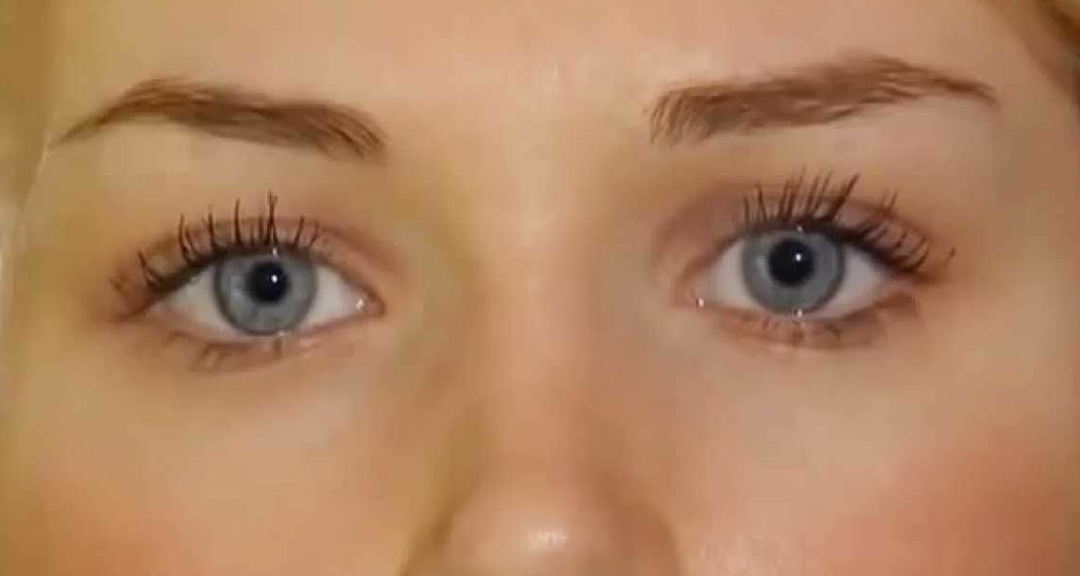
The concept of beauty has always been a subject of fascination and debate across cultures and eras. In recent years, scientific studies have attempted to define what makes a face beautiful, using various parameters and mathematical equations. The quest to identify the "scientifically most beautiful face" not only intrigues artists and designers but also psychologists and biologists. This article delves into the scientific principles behind beauty, highlighting key studies and findings that contribute to our understanding of facial attractiveness.
In this comprehensive exploration, we will discuss the measurement of beauty through the lens of science, the role of symmetry, proportion, and other factors that contribute to the perception of an attractive face. We will also examine how these principles have been applied in real-world scenarios, from art to media. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper appreciation of the science behind beauty and the factors that contribute to the ideal face.
We will provide valuable insights, backed by research and expert opinions, ensuring that you leave with a wealth of knowledge that can enhance your understanding of beauty. Whether you're an aspiring artist, a psychology enthusiast, or simply curious about the science of beauty, this article is designed to engage and inform you thoroughly.
Table of Contents
- What is Beauty?
- The Science of Beauty
- The Role of Symmetry in Attractiveness
- Understanding the Golden Ratio
- Cultural Variations in Beauty Standards
- The Scientifically Most Beautiful Face
- Real-World Applications of Beauty Science
- Conclusion
What is Beauty?
Beauty is a complex and multifaceted concept that encompasses not only physical appearance but also emotional and psychological facets. Philosophers have debated the nature of beauty for centuries, leading to various interpretations. In modern times, beauty is often associated with specific traits, such as symmetry, proportion, and harmony.
There are several theories of beauty, including:
- Subjective Theory: Beauty is in the eye of the beholder; each person's perception is unique.
- Objective Theory: Certain qualities can be universally recognized as beautiful.
- Evolutionary Theory: Attraction is linked to reproductive fitness, where certain traits indicate health and genetic quality.
The Science of Beauty
Recent scientific research has sought to quantify beauty using mathematical models and psychological tests. A prominent study by researchers at the University of Toronto used facial recognition software to analyze faces and determine which traits are most commonly associated with beauty.
Key findings from various studies include:
- Facial Symmetry: Faces that are more symmetrical are often rated as more attractive.
- Proportionality: The proportions of facial features, such as the distance between the eyes and the width of the mouth, can influence attractiveness.
- Skin Clarity: Clear, smooth skin is often associated with youth and beauty.
The Role of Symmetry in Attractiveness
Symmetry plays a crucial role in the perception of beauty. Numerous studies have shown that symmetrical faces tend to be rated as more attractive than asymmetrical ones. This phenomenon is often linked to evolutionary biology; symmetrical features may indicate genetic health and fitness.
Researchers have conducted experiments to assess the impact of symmetry on attractiveness:
- Participants consistently rated symmetrical faces higher than asymmetrical ones.
- Facial symmetry is often associated with youth and overall health.
Understanding the Golden Ratio
The Golden Ratio, approximately 1.618, has been a foundational concept in art and architecture for centuries. This mathematical ratio is believed to contribute to aesthetic appeal, and it also applies to human faces. The ideal face is often said to embody proportions that align with the Golden Ratio.
Key aspects of the Golden Ratio in facial beauty include:
- The ideal distance between the eyes should be one-fifth the width of the face.
- The length of the face should be approximately 1.5 times the width.
- Facial features, such as the nose and lips, should also conform to the Golden Ratio for optimal attractiveness.
Cultural Variations in Beauty Standards
Beauty is not a one-size-fits-all concept; it varies significantly across cultures. What is considered beautiful in one culture may not hold the same value in another. Historical and cultural contexts shape perceptions of beauty, leading to diverse standards and ideals.
Examples of cultural beauty standards include:
- In some African cultures, body adornments and scarification are seen as symbols of beauty.
- In Western cultures, features such as a slim figure and clear skin are often idealized.
- In East Asian cultures, lighter skin is often preferred, reflecting historical associations with social status.
The Scientifically Most Beautiful Face
Several studies have attempted to create a composite of the "most beautiful face" by blending features from various individuals deemed attractive. One notable example is the work by Dr. Julian De Silva, who used computer algorithms to analyze the facial features of celebrities and create a composite image of the ideal face.
The characteristics of this scientifically created beautiful face often include:
- High cheekbones
- A well-defined jawline
- Full lips
- Symmetrical features
- A balanced forehead-to-chin ratio
Real-World Applications of Beauty Science
The science of beauty extends beyond personal attraction; it has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Cosmetics: Understanding the principles of beauty has influenced product development and marketing strategies.
- Plastic Surgery: Surgeons often use principles of attractiveness to guide procedures aimed at enhancing facial features.
- Media and Advertising: Brands utilize beauty standards to create appealing marketing campaigns and advertisements.
Conclusion
In summary, the concept of the scientifically most beautiful face is grounded in a blend of mathematics, psychology, and cultural perspectives. Factors such as symmetry, proportion, and clarity of skin play significant roles in shaping our perceptions of beauty. Understanding these principles can enhance our appreciation for the complexities of human attractiveness.
As you reflect on the science of beauty, consider how these insights might influence your own perceptions and values. We invite you to leave a comment with your thoughts, share this article with others, or explore more content on our site.
Penutup
Thank you for exploring the fascinating world of beauty science with us. We hope you found this article informative and engaging. We look forward to welcoming you back for more insightful discussions in the future!